2020 Security Vulnerability Report
CVE Statistics for 2020
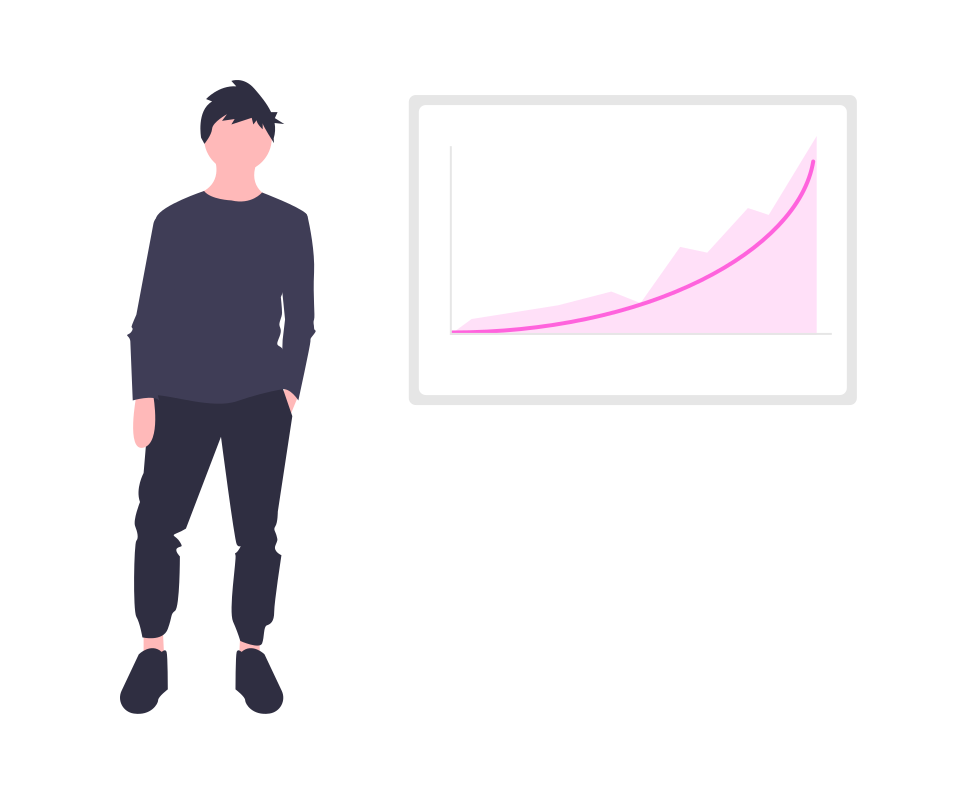

The average severity was 7.1 out of 10, which decreased by 0.1 from 2019.
Products & Vendors with the most security vulnerabilities published in 2020 Vulnerabilities may exist in multiple products or vendors
By Product
By Vendor
By Weakness
#1
XSS
The software does not neutralize or incorrectly neutralizes user-controllable input before it is placed in output that is used as a web page that is served to other users.#2
Memory Corruption
The software writes data past the end, or before the beginning, of the intended buffer. Typically, this can result in corruption of data, a crash, or code execution. The software may modify an index or perform pointer arithmetic that references a memory location that is outside of the boundaries of the buffer. A subsequent write operation then produces undefined or unexpected results.#3
Improper Input Validation
The product receives input or data, but it does not validate or incorrectly validates that the input has the properties that are required to process the data safely and correctly.#4
Improper Privilege Management
The software does not properly assign, modify, track, or check privileges for an actor, creating an unintended sphere of control for that actor.#5
Information Disclosure
The product exposes sensitive information to an actor that is not explicitly authorized to have access to that information.#6
Out-of-bounds Read
The software reads data past the end, or before the beginning, of the intended buffer. Typically, this can allow attackers to read sensitive information from other memory locations or cause a crash. A crash can occur when the code reads a variable amount of data and assumes that a sentinel exists to stop the read operation, such as a NUL in a string. The expected sentinel might not be located in the out-of-bounds memory, causing excessive data to be read, leading to a segmentation fault or a buffer overflow. The software may modify an index or perform pointer arithmetic that references a memory location that is outside of the boundaries of the buffer. A subsequent read operation then produces undefined or unexpected results.#7
Shell injection
The software constructs all or part of an OS command using externally-influenced input from an upstream component, but it does not neutralize or incorrectly neutralizes special elements that could modify the intended OS command when it is sent to a downstream component.#8
SQL Injection
The software constructs all or part of an SQL command using externally-influenced input from an upstream component, but it does not neutralize or incorrectly neutralizes special elements that could modify the intended SQL command when it is sent to a downstream component.#9
Directory traversal
The software uses external input to construct a pathname that is intended to identify a file or directory that is located underneath a restricted parent directory, but the software does not properly neutralize special elements within the pathname that can cause the pathname to resolve to a location that is outside of the restricted directory.#10
Buffer Overflow
The software performs operations on a memory buffer, but it can read from or write to a memory location that is outside of the intended boundary of the buffer.#11
Classic Buffer Overflow
The program copies an input buffer to an output buffer without verifying that the size of the input buffer is less than the size of the output buffer, leading to a buffer overflow. A buffer overflow condition exists when a program attempts to put more data in a buffer than it can hold, or when a program attempts to put data in a memory area outside of the boundaries of a buffer. The simplest type of error, and the most common cause of buffer overflows, is the "classic" case in which the program copies the buffer without restricting how much is copied. Other variants exist, but the existence of a classic overflow strongly suggests that the programmer is not considering even the most basic of security protections.#12
Session Riding
The web application does not, or can not, sufficiently verify whether a well-formed, valid, consistent request was intentionally provided by the user who submitted the request. When a web server is designed to receive a request from a client without any mechanism for verifying that it was intentionally sent, then it might be possible for an attacker to trick a client into making an unintentional request to the web server which will be treated as an authentic request. This can be done via a URL, image load, XMLHttpRequest, etc. and can result in exposure of data or unintended code execution.#13
Dangling pointer
Referencing memory after it has been freed can cause a program to crash, use unexpected values, or execute code.#14
authentification
When an actor claims to have a given identity, the software does not prove or insufficiently proves that the claim is correct.#15
Injection
The software constructs all or part of a command, data structure, or record using externally-influenced input from an upstream component, but it does not neutralize or incorrectly neutralizes special elements that could modify how it is parsed or interpreted when it is sent to a downstream component. Software has certain assumptions about what constitutes data and control respectively. It is the lack of verification of these assumptions for user-controlled input that leads to injection problems. Injection problems encompass a wide variety of issues -- all mitigated in very different ways and usually attempted in order to alter the control flow of the process. For this reason, the most effective way to discuss these weaknesses is to note the distinct features which classify them as injection weaknesses. The most important issue to note is that all injection problems share one thing in common -- i.e., they allow for the injection of control plane data into the user-controlled data plane. This means that the execution of the process may be altered by sending code in through legitimate data channels, using no other mechanism. While buffer overflows, and many other flaws, involve the use of some further issue to gain execution, injection problems need only for the data to be parsed. The most classic instantiations of this category of weakness are SQL injection and format string vulnerabilities.#16
AuthZ
The software performs an authorization check when an actor attempts to access a resource or perform an action, but it does not correctly perform the check. This allows attackers to bypass intended access restrictions.#17
Incorrect Default Permissions
During installation, installed file permissions are set to allow anyone to modify those files.#18
Resource Exhaustion
The software does not properly control the allocation and maintenance of a limited resource, thereby enabling an actor to influence the amount of resources consumed, eventually leading to the exhaustion of available resources.#19
Insufficiently Protected Credentials
The product transmits or stores authentication credentials, but it uses an insecure method that is susceptible to unauthorized interception and/or retrieval.#20
AuthZ
The software does not perform an authorization check when an actor attempts to access a resource or perform an action.#21
Unrestricted File Upload
The software allows the attacker to upload or transfer files of dangerous types that can be automatically processed within the product's environment.#22
Incorrect Permission Assignment for Critical Resource
The product specifies permissions for a security-critical resource in a way that allows that resource to be read or modified by unintended actors. When a resource is given a permissions setting that provides access to a wider range of actors than required, it could lead to the exposure of sensitive information, or the modification of that resource by unintended parties. This is especially dangerous when the resource is related to program configuration, execution or sensitive user data.#23
Use of Hard-coded Credentials
The software contains hard-coded credentials, such as a password or cryptographic key, which it uses for its own inbound authentication, outbound communication to external components, or encryption of internal data.#24
NULL Pointer Dereference
A NULL pointer dereference occurs when the application dereferences a pointer that it expects to be valid, but is NULL, typically causing a crash or exit. NULL pointer dereference issues can occur through a number of flaws, including race conditions, and simple programming omissions.#25
Missing Authentication for Critical Function
The software does not perform any authentication for functionality that requires a provable user identity or consumes a significant amount of resources.By Category
Fortinet FortiClient
8 vulnerabilities in 2020
Fortinet FortiOS
7 vulnerabilities in 2020
Apache NiFi
6 vulnerabilities in 2020
Content Management
Joomla
31 vulnerabilities in 2020
MediaWiki
30 vulnerabilities in 2020
Adobe Experience Manager
24 vulnerabilities in 2020
Database
Oracle MySQL
139 vulnerabilities in 2020
Oracle Database Server
15 vulnerabilities in 2020
MariaDB
15 vulnerabilities in 2020
Desktop Software
Apple iTunes
85 vulnerabilities in 2020
Mozilla Thunderbird
76 vulnerabilities in 2020
Microsoft Office
71 vulnerabilities in 2020
Development Tools
Oracle Java Development Kit (JDK)
41 vulnerabilities in 2020
Jenkins
19 vulnerabilities in 2020
Microsoft Visual Studio
10 vulnerabilities in 2020
DevOps
GitLab
235 vulnerabilities in 2020
Kubernetes
13 vulnerabilities in 2020
Docker
4 vulnerabilities in 2020
Microsoft Exchange Server
14 vulnerabilities in 2020
Exim
1 vulnerability in 2020
Postfix
1 vulnerability in 2020
Java Application Servers
Oracle Weblogic Server
69 vulnerabilities in 2020
IBM WebSphere Application Server
22 vulnerabilities in 2020
Apache Tomcat
9 vulnerabilities in 2020
Java Libraries
FasterXML Jackson Databind
26 vulnerabilities in 2020
Libraries
Google Tensorflow
35 vulnerabilities in 2020
Microsoft ChakraCore
32 vulnerabilities in 2020
Apache AirFlow
12 vulnerabilities in 2020
Mobile Applications
Apple Music
1 vulnerability in 2020
Operating Systems
Debian Linux
1039 vulnerabilities in 2020
Microsoft Windows 10
792 vulnerabilities in 2020
Microsoft Windows Server 2016
788 vulnerabilities in 2020
Runtime Environments
Oracle Java Runtime Environment (JRE)
39 vulnerabilities in 2020
Oracle OpenJDK
36 vulnerabilities in 2020
nodejs node.js
14 vulnerabilities in 2020
Server Software
Microsoft Sharepoint Server
113 vulnerabilities in 2020
Microsoft Sharepoint Enterprise Server
106 vulnerabilities in 2020
OpenBSD OpenSSH
3 vulnerabilities in 2020
Virtualization
Oracle VM VirtualBox
69 vulnerabilities in 2020
QEMU
42 vulnerabilities in 2020
Citrix Xen Desktop
2 vulnerabilities in 2020
Web Application Framework
Django Project Django
6 vulnerabilities in 2020
Microsoft ASP.NET Core
5 vulnerabilities in 2020
Laravel
2 vulnerabilities in 2020
Web Applications
Apple iCloud
86 vulnerabilities in 2020
Adobe Magento
1 vulnerability in 2020
Web Browsers
Google Chrome
227 vulnerabilities in 2020
Mozilla Firefox
132 vulnerabilities in 2020
Mozilla FireFox Extended Support Release (ESR)
73 vulnerabilities in 2020
Web Servers
Apache HTTP Server
6 vulnerabilities in 2020
Caddy Server Caddy Web Server
1 vulnerability in 2020
2020 Known Exploited Vulnerabilities
These vulnerabilities may be considered some of the most dangerous vulnerabilities of 2020, because they are both known to have been exploited and have a high severity score. In fact 5 vulnerabilities scored the highest possible CVSS base score, of 10.
CVE-2020-0796 vulnerability in SMBv3, disclosed on March 12, 2020
CVE-2020-6287 vulnerability in SAP NetWeaver AS JAVA (LM Configuration Wizard), disclosed on July 14, 2020
CVE-2020-1350 vulnerability in Windows, disclosed on July 14, 2020
CVE-2020-14871 vulnerability in Oracle Solaris, disclosed on October 21, 2020
CVE-2020-2021 vulnerability in PAN-OS, disclosed on June 29, 2020
CVE-2020-1938 vulnerability in Tomcat, disclosed on February 24, 2020
CVE-2020-14882 vulnerability in Oracle WebLogic Server, disclosed on October 21, 2020
CVE-2020-5902 vulnerability in BIG-IP, disclosed on July 1, 2020
CVE-2020-14750 vulnerability in Oracle WebLogic Server, disclosed on November 2, 2020
CVE-2020-25223 vulnerability in SG UTM, disclosed on September 25, 2020
CVE-2020-7961 vulnerability in Liferay Portal, disclosed on March 20, 2020
CVE-2020-25213 vulnerability in File Manager, disclosed on September 9, 2020
CVE-2020-17530 vulnerability in Struts, disclosed on December 11, 2020
CVE-2020-2551 vulnerability in Fusion Middleware, disclosed on January 15, 2020
CVE-2020-15505 vulnerability in MobileIron Core & Connector, disclosed on July 7, 2020
CVE-2020-16846 vulnerability in Salt, disclosed on November 6, 2020
CVE-2020-11651 vulnerability in Salt, disclosed on April 30, 2020
CVE-2020-8515 vulnerability in Vigor Router(s), disclosed on February 1, 2020
CVE-2020-10148 vulnerability in SolarWinds Orion Platform, disclosed on December 29, 2020
CVE-2020-6207 vulnerability in SAP Solution Manager (User Experience Monitoring), disclosed on March 10, 2020
CVE-2020-9054 vulnerability in Multiple Network-Attached Storage (NAS) Devices, disclosed on March 4, 2020
CVE-2020-10189 vulnerability in ManageEngine Desktop Central, disclosed on March 6, 2020
CVE-2020-29583 vulnerability in Unified Security Gateway (USG), disclosed on December 22, 2020
CVE-2020-13927 vulnerability in Airflow's Experimental API, disclosed on November 10, 2020
CVE-2020-7247 vulnerability in OpenSMTPD, disclosed on January 29, 2020
CVE-2020-17496 vulnerability in vBulletin, disclosed on August 12, 2020
CVE-2020-2883 vulnerability in WebLogic Server, disclosed on April 15, 2020
CVE-2020-12641 vulnerability in Roundcube Webmail, disclosed on May 4, 2020
CVE-2020-5847 vulnerability in Unraid, disclosed on March 16, 2020
CVE-2020-8644 vulnerability in PlaySMS, disclosed on February 5, 2020
CVE-2020-10987 vulnerability in Tenda AC15 AC1900, disclosed on July 13, 2020
CVE-2020-3952 vulnerability in vCenter Server, disclosed on April 10, 2020
CVE-2020-2555 vulnerability in Oracle Coherence, disclosed on January 15, 2020
CVE-2020-0646 vulnerability in Microsoft .NET Framework, disclosed on January 14, 2020
CVE-2020-15415 vulnerability in Multiple Vigor Routers, disclosed on June 30, 2020
CVE-2020-26919 vulnerability in NETGEAR JGS516PE devices, disclosed on October 9, 2020
CVE-2020-5722 vulnerability in UCM6200, disclosed on March 23, 2020
CVE-2020-3992 vulnerability in ESXi, disclosed on October 20, 2020
CVE-2020-14644 vulnerability in WebLogic Server, disclosed on July 15, 2020
CVE-2020-8657 vulnerability in EyesOfNetwork, disclosed on February 6, 2020
CVE-2020-12271 vulnerability in Sophos XG Firewall devices, disclosed on April 27, 2020
CVE-2020-3161 vulnerability in IP Phones, disclosed on April 15, 2020
CVE-2020-15069 vulnerability in XG Firewall, disclosed on June 29, 2020
CVE-2020-8599 vulnerability in Trend Micro Apex One and OfficeScan XG server, disclosed on March 18, 2020
CVE-2018-19949 vulnerability in Network Attached Storage (NAS), disclosed on October 28, 2020
CVE-2020-4427 vulnerability in IBM Data Risk Manager, disclosed on May 7, 2020
CVE-2020-12812 vulnerability in FortiOS, disclosed on July 24, 2020
CVE-2020-5135 vulnerability in SonicOS, disclosed on October 12, 2020
CVE-2020-10181 vulnerability in Sumavision Enhanced Multimedia Router (EMR), disclosed on March 11, 2020
CVE-2020-29574 vulnerability in CyberoamOS, disclosed on December 11, 2020
CVE-2020-17463 vulnerability in , disclosed on August 13, 2020
CVE-2020-1631 vulnerability in Junos OS, disclosed on May 4, 2020
CVE-2020-15999 vulnerability in Chrome, disclosed on November 3, 2020
CVE-2020-4428 vulnerability in IBM Data Risk Manager, disclosed on May 7, 2020
CVE-2020-4006 vulnerability in VMware Workspace One Access, Access Connector, Identity Manager, and Identity Manager Connector, disclosed on November 23, 2020
CVE-2020-1040 vulnerability in Hyper-V RemoteFX vGPU, disclosed on July 14, 2020
CVE-2020-0688 vulnerability in Microsoft Exchange Server, disclosed on February 11, 2020
CVE-2020-11978 vulnerability in Airflow, disclosed on July 17, 2020
CVE-2020-0618 vulnerability in SQL Server, disclosed on February 11, 2020
CVE-2020-10199 vulnerability in Sonatype Nexus Repository, disclosed on April 1, 2020
CVE-2020-1956 vulnerability in Kylin, disclosed on May 22, 2020
CVE-2020-10221 vulnerability in rConfig, disclosed on March 8, 2020
CVE-2020-1020 vulnerability in Windows, Windows Adobe Type Manager Library, disclosed on April 15, 2020
CVE-2020-6418 vulnerability in Chromium V8 Engine, disclosed on February 27, 2020
CVE-2020-16009 vulnerability in Chromium V8 Engine, disclosed on November 3, 2020
CVE-2020-9377 vulnerability in DIR-610 Devices, disclosed on July 9, 2020
CVE-2020-5735 vulnerability in Cameras and Network Video Recorder (NVR), disclosed on April 8, 2020
CVE-2019-17026 vulnerability in IonMonkey JIT compiler, disclosed on March 2, 2020
CVE-2020-16010 vulnerability in Chrome for Android, disclosed on November 3, 2020
CVE-2020-8467 vulnerability in Trend Micro Apex One and OfficeScan XG, disclosed on March 18, 2020
CVE-2020-13671 vulnerability in Drupal core, disclosed on November 20, 2020
CVE-2020-8468 vulnerability in Trend Micro Apex One, OfficeScan XG and Worry-Free Business Security, disclosed on March 18, 2020
CVE-2020-9818 vulnerability in iOS Mail, disclosed on June 9, 2020
CVE-2020-3118 vulnerability in IOS XR, disclosed on February 5, 2020
CVE-2020-3569 vulnerability in IOS XR, disclosed on September 23, 2020
CVE-2020-3566 vulnerability in IOS XR, disclosed on August 29, 2020
CVE-2020-17144 vulnerability in Microsoft Exchange Server, disclosed on December 10, 2020
CVE-2019-18426 vulnerability in WhatsApp, disclosed on January 21, 2020
CVE-2020-0601 vulnerability in Windows CryptoAPI, disclosed on January 14, 2020
CVE-2020-6820 vulnerability in ReadableStream, disclosed on April 24, 2020
CVE-2020-6819 vulnerability in nsDocShell destructor, disclosed on April 24, 2020
CVE-2019-20500 vulnerability in DWL-2600AP Access Point, disclosed on March 5, 2020
CVE-2020-28949 vulnerability in Archive_Tar, disclosed on November 19, 2020
CVE-2020-1147 vulnerability in Microsoft .NET Framework, Microsoft SharePoint, Visual Studio, disclosed on July 14, 2020
CVE-2020-0938 vulnerability in Windows, Windows Adobe Type Manager Library, disclosed on April 15, 2020
CVE-2020-1380 vulnerability in Internet Explorer, disclosed on August 17, 2020
CVE-2020-8655 vulnerability in EyesOfNetwork, disclosed on February 7, 2020
CVE-2020-1054 vulnerability in Win32k, disclosed on May 21, 2020
CVE-2020-0787 vulnerability in Windows, disclosed on March 12, 2020
CVE-2020-27930 vulnerability in iOS and macOS, disclosed on December 8, 2020
CVE-2020-0683 vulnerability in Windows, disclosed on February 11, 2020
CVE-2020-0041 vulnerability in Android OS, disclosed on March 10, 2020
CVE-2020-0986 vulnerability in Windows, disclosed on June 9, 2020
CVE-2020-17087 vulnerability in Windows, disclosed on November 11, 2020
CVE-2020-1027 vulnerability in Windows, disclosed on April 15, 2020
CVE-2020-3950 vulnerability in VMware Fusion, VMware Remote Console for Mac, and Horizon Client for Mac, disclosed on March 17, 2020
CVE-2020-3837 vulnerability in Multiple Products, disclosed on February 27, 2020
CVE-2020-0638 vulnerability in Update Notification Manager, disclosed on January 14, 2020
CVE-2020-3433 vulnerability in AnyConnect Secure, disclosed on August 17, 2020
CVE-2020-1464 vulnerability in Windows, disclosed on August 17, 2020
Report Last Updated: July 13, 2025