2022 Security Vulnerability Report
CVE Statistics for 2022
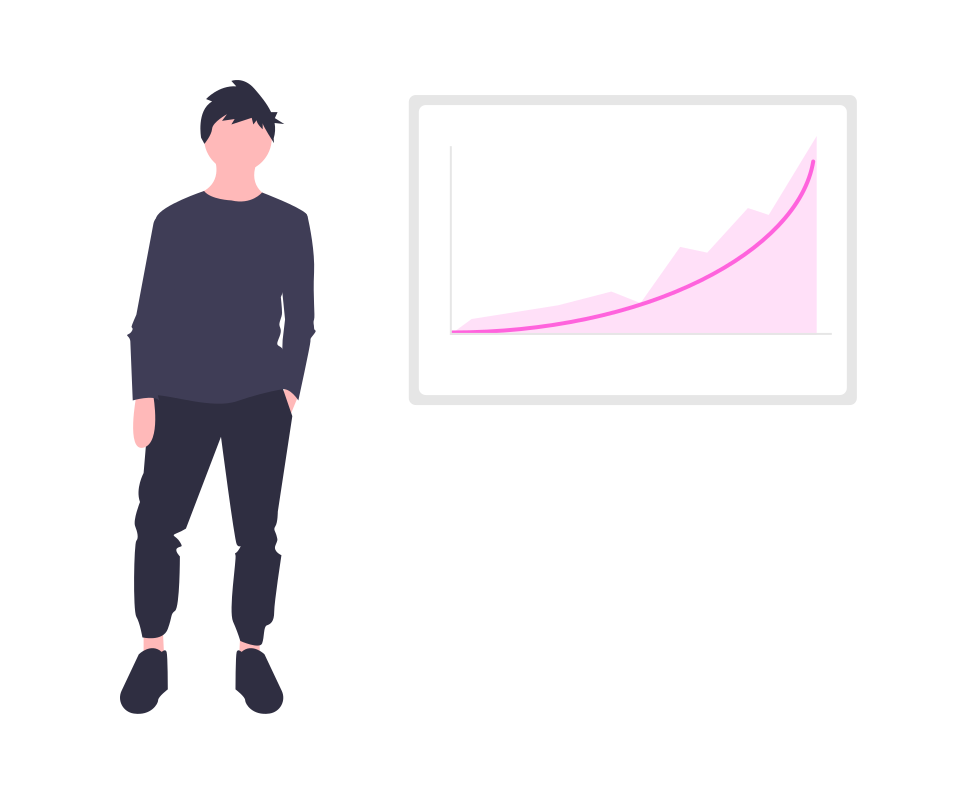

There were 25072 security vulnerabilities (CVEs) published in 2022. In 2021 there were 20194.
The average severity was 7.2 out of 10, up by 0.1 from 2021.
The average severity was 7.2 out of 10, up by 0.1 from 2021.
Products & Vendors with the most security vulnerabilities published in 2022 Vulnerabilities may exist in multiple products or vendors
By Product
By Vendor
By Weakness
#1
XSS
The software does not neutralize or incorrectly neutralizes user-controllable input before it is placed in output that is used as a web page that is served to other users.
3262
#2
Memory Corruption
The software writes data past the end, or before the beginning, of the intended buffer. Typically, this can result in corruption of data, a crash, or code execution. The software may modify an index or perform pointer arithmetic that references a memory location that is outside of the boundaries of the buffer. A subsequent write operation then produces undefined or unexpected results.
2086
#3
SQL Injection
The software constructs all or part of an SQL command using externally-influenced input from an upstream component, but it does not neutralize or incorrectly neutralizes special elements that could modify the intended SQL command when it is sent to a downstream component.
1771
#4
Out-of-bounds Read
The software reads data past the end, or before the beginning, of the intended buffer. Typically, this can allow attackers to read sensitive information from other memory locations or cause a crash. A crash can occur when the code reads a variable amount of data and assumes that a sentinel exists to stop the read operation, such as a NUL in a string. The expected sentinel might not be located in the out-of-bounds memory, causing excessive data to be read, leading to a segmentation fault or a buffer overflow. The software may modify an index or perform pointer arithmetic that references a memory location that is outside of the boundaries of the buffer. A subsequent read operation then produces undefined or unexpected results.
785
#5
Directory traversal
The software uses external input to construct a pathname that is intended to identify a file or directory that is located underneath a restricted parent directory, but the software does not properly neutralize special elements within the pathname that can cause the pathname to resolve to a location that is outside of the restricted directory.
720
#6
Session Riding
The web application does not, or can not, sufficiently verify whether a well-formed, valid, consistent request was intentionally provided by the user who submitted the request. When a web server is designed to receive a request from a client without any mechanism for verifying that it was intentionally sent, then it might be possible for an attacker to trick a client into making an unintentional request to the web server which will be treated as an authentic request. This can be done via a URL, image load, XMLHttpRequest, etc. and can result in exposure of data or unintended code execution.
704
#7
Dangling pointer
Referencing memory after it has been freed can cause a program to crash, use unexpected values, or execute code.
686
#8
Shell injection
The software constructs all or part of an OS command using externally-influenced input from an upstream component, but it does not neutralize or incorrectly neutralizes special elements that could modify the intended OS command when it is sent to a downstream component.
551
#9
Improper Input Validation
The product receives input or data, but it does not validate or incorrectly validates that the input has the properties that are required to process the data safely and correctly.
542
#10
Unrestricted File Upload
The software allows the attacker to upload or transfer files of dangerous types that can be automatically processed within the product's environment.
462
#11
AuthZ
The software does not perform an authorization check when an actor attempts to access a resource or perform an action.
435
#12
Classic Buffer Overflow
The program copies an input buffer to an output buffer without verifying that the size of the input buffer is less than the size of the output buffer, leading to a buffer overflow. A buffer overflow condition exists when a program attempts to put more data in a buffer than it can hold, or when a program attempts to put data in a memory area outside of the boundaries of a buffer. The simplest type of error, and the most common cause of buffer overflows, is the "classic" case in which the program copies the buffer without restricting how much is copied. Other variants exist, but the existence of a classic overflow strongly suggests that the programmer is not considering even the most basic of security protections.
402
#13
NULL Pointer Dereference
A NULL pointer dereference occurs when the application dereferences a pointer that it expects to be valid, but is NULL, typically causing a crash or exit. NULL pointer dereference issues can occur through a number of flaws, including race conditions, and simple programming omissions.
374
#14
authentification
When an actor claims to have a given identity, the software does not prove or insufficiently proves that the claim is correct.
340
#15
Race Condition
The program contains a code sequence that can run concurrently with other code, and the code sequence requires temporary, exclusive access to a shared resource, but a timing window exists in which the shared resource can be modified by another code sequence that is operating concurrently.
229
#16
AuthZ
The software performs an authorization check when an actor attempts to access a resource or perform an action, but it does not correctly perform the check. This allows attackers to bypass intended access restrictions.
226
#17
Integer Overflow or Wraparound
The software performs a calculation that can produce an integer overflow or wraparound, when the logic assumes that the resulting value will always be larger than the original value. This can introduce other weaknesses when the calculation is used for resource management or execution control. An integer overflow or wraparound occurs when an integer value is incremented to a value that is too large to store in the associated representation. When this occurs, the value may wrap to become a very small or negative number. While this may be intended behavior in circumstances that rely on wrapping, it can have security consequences if the wrap is unexpected. This is especially the case if the integer overflow can be triggered using user-supplied inputs. This becomes security-critical when the result is used to control looping, make a security decision, or determine the offset or size in behaviors such as memory allocation, copying, concatenation, etc.
223
#18
Buffer Overflow
The software performs operations on a memory buffer, but it can read from or write to a memory location that is outside of the intended boundary of the buffer.
206
#19
SSRF
The web server receives a URL or similar request from an upstream component and retrieves the contents of this URL, but it does not sufficiently ensure that the request is being sent to the expected destination. By providing URLs to unexpected hosts or ports, attackers can make it appear that the server is sending the request, possibly bypassing access controls such as firewalls that prevent the attackers from accessing the URLs directly. The server can be used as a proxy to conduct port scanning of hosts in internal networks, use other URLs such as that can access documents on the system (using file://), or use other protocols such as gopher:// or tftp://, which may provide greater control over the contents of requests.
205
#20
Use of Hard-coded Credentials
The software contains hard-coded credentials, such as a password or cryptographic key, which it uses for its own inbound authentication, outbound communication to external components, or encryption of internal data.
195
#21
Missing Authentication for Critical Function
The software does not perform any authentication for functionality that requires a provable user identity or consumes a significant amount of resources.
193
#22
Command Injection
The software constructs all or part of a command using externally-influenced input from an upstream component, but it does not neutralize or incorrectly neutralizes special elements that could modify the intended command when it is sent to a downstream component.
193
#23
Improper Privilege Management
The software does not properly assign, modify, track, or check privileges for an actor, creating an unintended sphere of control for that actor.
192
#24
Incorrect Default Permissions
During installation, installed file permissions are set to allow anyone to modify those files.
180
#25
Information Disclosure
The product exposes sensitive information to an actor that is not explicitly authorized to have access to that information.
179